HISTORY OF GLOBAL MARKET INTEGRATION
The idea of global market is not new to us. As time and years passed, we people continue to connect and communicate with other people up until now. The modern technologies and devices are critical nowadays since it helps us to have a better access to share one country's products, devices and even cultures. As we continue to acknowledge, amaze and influence by other countries products, we tends to import their products and sell it in a price similar with other locations. This kind of action is now an example of global market integration.
However, even though we are practicing this kind of concept, some of us still didn't know the real definition and the history of Global Market Integration. How it is started? How does it reach to us? You may asked. It was said that there are three revolutions regarding the history of Global Market Integration.
This blog will discuss and share information about the definition and the history of Global Market integration. Let's first define the definition of Global Market Integration.
Remember that when prices in several areas or hoods follow similar patterns over time, this is referred as market integration. The marketplaces are said to be integrated when groups of items move proportionally to each other. It's also possible to argue that market integration is a metric that explains how interconnected different marketplaces are.
A Coca-Cola company is an example of market integration. The Coca-Cola Company was founded in 1886 and has maintained the same pricing for a long time, distributing to US country until it has expanded to over 200 countries across the world. This corporation attempted to provide beverages at a low cost in order to grow their business into other countries. They ensure that the price is marketable to the same foreign countries since, as we all know that in different countries they have also different cultures and buying customs. That is why it is advisable to develop plans and techniques in order to move from one country to another.
Now, since we already know the definition of global market integration let's now discuss the history or the origin of global market integration. Such as how does it reach to our generation? Or how it is started? These are the common questions that might appears in your mind.
The History of Global Market Integration
People exclusively produced food for their families prior to the development of the modern economy. In today's economy, multiple sectors must collaborate to manufacture, distribute, and exchange products and services. What is the reason for this shift in how individuals create for their needs? Let us now travel back in time 12,000 years.
In the history of Global Market integration, there are three revolutions which we get through before we experience the recent global market integration. These are the three revolutions:
* Agricultural Revolution
* Industrial Revolution
* Information Revolution
Let's first discuss the first revolution of Global Market integration which is the Agricultural Revolution.
1. Agricultural Revolution
- Agricultural revolution is the first major economic development, according to (Pomeranz, 2000). People discovered that domesticating plants and animals was more productive than hunter-gatherer communities when they learnt how to do so. In this revolution the new agricultural economy was born. Farming enabled cultures to create surpluses, allowing people to spend less time producing food. This resulted in significant changes such as permanent settlements, trade networks, and population increase.
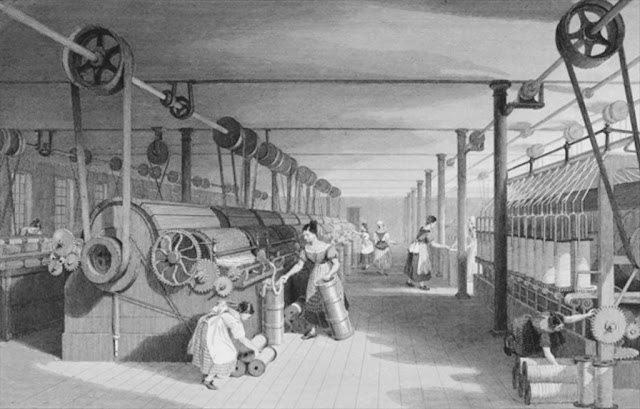
2. Industrial Revolution
- The next is the industrial revolution, which has already begun with the invention of machines. In the 1800s, this was a second significant economic revolution. New economic tools such as steam engines, manufacturing, and mass production appeared as the industry grew. Factories arose, and job functions shifted. Instead of working from home as they had done previously, they began working as wage workers, eventually becoming more adept and mastering their talents in their chosen sector. Because of mass manufacturing, productivity increased, living standards improved, and people had access to a wider range of goods.
Under this revolution, there are two competing economic models during the industrial revolution. These are the Capitalism and Socialism.
1. Capitalism
- It is a system in which all natural resources and production means are held by private individuals. Profit maximization and competitiveness are emphasized as the primary drivers of efficiency. Naturally, if you are competing, you would devise plans and techniques to improve your efficiency. This means that in order to flourish as a business owner, you must surpass your competition. It is advisable that he is motivated to be more efficient by enhancing the product's quality and lowering its cost.
So, if you look at the image above, we can see that people in capitalism are not working. However if we look at the people on the left side, we can say that they are in need of jobs and they are the skilled one. This gives us an idea that these people are the most talented and workaholic people who are applying for the company, but the owner of the company is the one who is gaining more profits. These individuals have a low income, yet they are working hard to advance in the firm. This is how capitalism works.
2. Socialism
- The means of production are owned by the entire community. It opposes capitalism's private property and laissez-faire attitude. Property is owned by the government and distributed to all citizens, not only those with the financial means to purchase it. It places a larger importance on providing everyone's basic needs than on individual profit, emphasizing community aims and expects everyone to contribute for the common good.
As we observed, these two types of competing economic models which are the Capitalism and Socialism has really do a big difference between each other.
• In capitalism, private individuals own the means of production, but in socialism, the public owns the means of production, such as money and other types of capita
• In capitalism, businesses exist just to make money; they live by the profit motive, but in socialism, everyone works for wealth, which is dispersed to al
Now, let proceed to the last revolution of the history of Global Market integration which is the Information Revolution
3. Information Revolution
- This revolution describe our recent global market integration where the rise of technology occur. Modern technology have lowered the importance of human labor and changed the economy away from manufacturing and toward service jobs and the production of ideas rather than products. As a result of the mass production, this has long-term economic consequences. This revolution is being driven by computer technology, and continued developments in that technology appear to ensure that this revolution will affect people's lives.
If you are one of the lucky person who have visited Lucky Me, or any well-known company, you'll see that machines are used in the manufacturing process. It appears that the role of human labor has been reduced. Also, as we can see on social media or through other channels, certain countries have opted to use robots rather than humans in the creation of their goods. As a result of these advancements in technology, robots can now do human-like tasks, boosting product productivity
I know that some of us are confused about global market integration, however through this blog you can gain knowledge regarding the history of Global Market integration. Now, that you know the history of Global Market Integration it will help you to have a better understanding to our recent situation. Hoping that this blog gives you more insight and information about the history of Global Market Integration. Thank you for reading.









Comments
Post a Comment